
Aluminium oxide - Al2O3
What is Aluminium Oxide (Al2O3)?
Al2O3 is an inorganic chemical reagent with chemical name Aluminium oxide. It is also called as Alpha-Alumina, alumina, alundum or aloxide.
Table of Contents
- Aluminium oxide Structure
- Properties of Aluminium oxide
- Chemical Properties of Aluminium Oxide
- Aluminium oxide Uses
- Frequently Asked Questions - FAQs
It is found naturally as corundum, Ruby’s, sapphires, and emeralds. It is an amphoteric substance, which reacts with both acids and bases. It occurs as solid and appears white. It is odourless and insoluble in water. The most common occurrence of this compound is in crystalline form, called α-aluminium oxide or corundum. Due to its hardness, is widely used and suitable to use as an abrasive and in cutting tools.
Aluminium oxide Structure
(Al2O3 Structure)
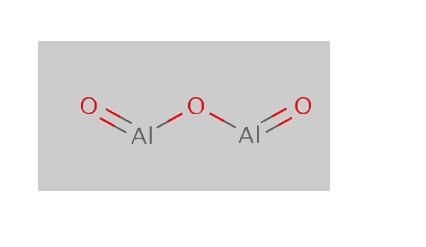
Properties of Aluminium oxide - Al2O3
Al2O3 Aluminium oxide Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass 101.96 g/mol Density 3.95 g/cm³ Boiling Point 2,977 °C Melting Point 2,072 °CChemical Properties of Aluminium Oxide
1. Reaction with sodium hydroxide
Aluminium oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide to produce sodium aluminate and water. This reaction takes place at a temperature of 900-1100°C. Salt and water are obtained in this reaction in which aluminium oxide acts as an acid.
Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
2. Reaction with sulphuric acid
Metal oxides are generally basic in nature but aluminium oxide is amphoteric oxide.
Hence it acts both as acid and base. In this case, it acts as a base
Al2O3 + H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + H2O
This is a neutralisation reaction.
3. Reaction with hydrochloric acid
Aluminium oxide contains oxide ions, and thus reacts with acids in the same way sodium or magnesium oxides do. Aluminium oxide reacts with hot dilute hydrochloric acid to give aluminium chloride solution.
Al2O3+6HCl → 2AlCl3+3H2O
Aluminium oxide (Al2O3 ) Uses
- Aluminium oxide is one of the common ingredients in sunscreen and is also present in cosmetics such as nail polish, blush, and lipstick.
- It is used in formulations of glass.
- It is used as a catalyst.
- It is used in the purification of water to remove water from the gas streams.
- It is used in sandpaper as an abrasive.
- Aluminium oxide is an electrical insulator used as a substrate for integrated circuits.
- Used in sodium vapour lamps.
Learn more about the chemical behaviour and importance of Aluminium oxide with the expert faculties at BYJU’S.
Other related links:
Conductors Types Of Catalyst
Link nội dung: https://giaidap.edu.vn/al203-ra-al-a75479.html